Kidney Biopsy Treatment in Ahmedabad
Kidney Biopsy: When It’s Needed
As a nephrologist, one of the most powerful tools we have to diagnose kidney diseases is the renal biopsy. This procedure helps determining the cause of kidney dysfunction, guiding treatment decisions, and predicting outcomes. Dr Kosha Patel the Best Nephrologist in Ahmedabad at her clinic provides the service of kidney biopsy and experienced with the procedure. However, as with any medical procedure, it’s important to understand when it’s necessary, how it’s performed, and the potential risks involved.
What is a Kidney Biopsy?
A renal biopsy involves taking a small sample of kidney tissue with the help of a permanent or a disposable needle for analysis under a microscope. The tissue is examined for signs of damage, inflammation, infection, or other abnormalities. This helps in diagnosing conditions such as glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, diabetic nephropathy, and Nephrotic state.

When is a Renal Biopsy Needed?
A renal biopsy is recommended when:
Unexplained kidney dysfunction
If blood or urine tests show abnormal kidney function (elevated creatinine, proteinuria, presence of blood cells in urine) a biopsy may help determine the underlying cause.
Diagnosis of specific kidney diseases
Certain kidney diseases can only be definitively diagnosed through a biopsy.
Monitoring disease progression
A biopsy can help assess the severity of damage in chronic kidney conditions and determine whether treatment is effective and whether the damage is reversible or not.
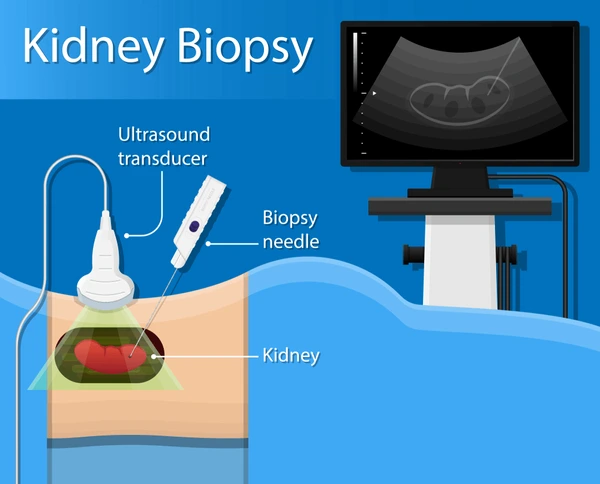
Renal Biopsy Procedure
Renal biopsies are usually performed using a percutaneous approach, which means inserting a needle through the skin to obtain the tissue sample. This is typically done under local anesthesia, and with the guidance of ultrasound to locate the kidney accurately under the guidance of our kidney specialist in Ahmedabad Dr Kosha Patel. In a small number of cases, the procedure might be done using a trans jugular biopsy, where a catheter is inserted through a vein in the neck to reach the kidney. This method is typically used when there are complications like obesity or when the patient has a bleeding disorder

What Happens After a Renal Biopsy?
Renal Biopsy is a day care procedure, After the procedure, patients are typically monitored for several hours in the hospital for any signs of bleeding or discomfort. Most people are able to go home the same day, though some may need to stay overnight for observation. It’s important to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for a week after the biopsy to minimize the risk of complications.
Risks and Complications
While a renal biopsy is generally safe, there are some risks to be aware of, including:
Bleeding
Kidney biopsies may cause bleeding due to high blood flow; rare cases might need transfusion.
Infection
Although rare, infections can occur at the biopsy site.
Pain
Mild back or belly pain may occur after the procedure but usually improves with pain relief.
Interpreting the Results
Once the kidney tissue is collected, it is sent to a pathologist for examination. The pathologist will look for various changes in the tissue, including inflammation, scarring, and the presence of certain immune cells. The biopsy results can provide a definitive diagnosis, such as:
Glomerulonephritis
Kidney filter inflammation, often from infection or autoimmune attack by the body’s own immune system.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD):
Chronic kidney damage, often irreversible, marked by scarring visible on examination.
Nephrotic syndrome
A group of symptoms that include severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and enema.
Why is a Renal Biopsy Important?
A renal biopsy can often reveal the precise cause of kidney dysfunction, allowing for more targeted and effective treatments. For example, certain forms of glomerulonephritis may respond well to immunosuppressive medications, while others might require more aggressive treatments like plasmapheresis. Without a biopsy, it would be difficult to tailor therapy to the specific condition affecting the kidneys.
Moreover, the biopsy results can help predict the course of kidney disease. In some cases, early intervention can prevent further damage to the kidneys and improve long-term outcomes.
Need Any Helps?
Get More Consultations

Frequently Asked Questions
What illnesses can be diagnosed with a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy aids in the diagnosis of conditions such as glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, diabetic kidney disease, kidney infection, and even kidney cancer. It also aids in screening for issues in transplanted kidneys.
Is a kidney biopsy a serious procedure?
It’s usually safe but still counted as delicate because it requires a small kidney sample being taken with a needle. That’s why it’s performed with caution in a hospital with close observation.
What are the contraindications for renal biopsy?
A biopsy is not performed if a person has bleeding problems, extremely high blood pressure, single kidney, or is on anticoagulants, as the risk of complications is greater.
What is a usual complication of a renal biopsy?
The most typical problem is bleeding, which presents as blood in the urine, typically mild and transient.
What is the cost of renal biopsy in Ahmedabad?
Dr Kosha patel, Expert kidney specialist in Ahmedabad offers kidney biopsy at affordable price. This depends on the patients condition , type of kidney problems and the anaesthesia required. The procedure cost around 7k to 15 K
What are the advantages of a biopsy?
It makes it easy for physicians to well understand the kidney issue, determine how dangerous it is and select the appropriate treatment to address it.
Working Hours
Monday to Saturday
09:00 AM to 09:00 PM
For Emergency
24 X 7
Your Kidney Health, Our Priority
