Peritoneal Dialysis in Ahmedabad
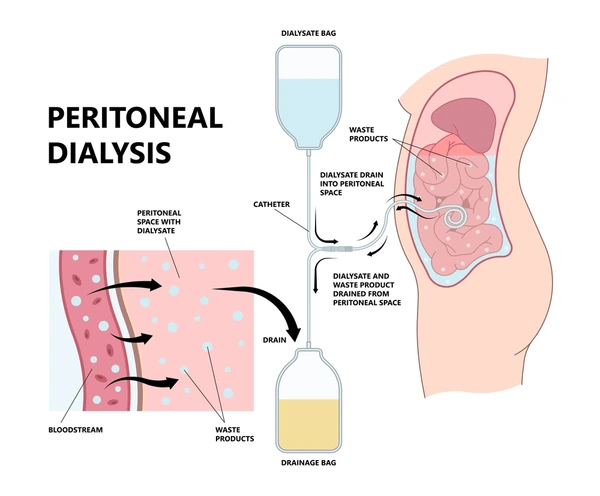
What is Peritoneal Dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment that uses the lining of the peritoneum inside the abdomen to filter waste, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood. Unlike hemodialysis, which relies on a machine, PD uses a sterile solution called dialysate that is introduced into the abdomen through a catheter. The solution absorbs waste and excess fluids from the blood vessels in the peritoneum, and after a few hours, it is drained away, carrying the waste with it. A nephrologist carefully guides patients through this process to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
This method is manual and performed by the patient or a caretaker 4-5 times daily and once at night. The patient will fill their abdomen with dialysate, let it stay for a few hours to absorb waste, and then drain it out.
Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
This is done with the help of a machine (cycler) that performs the exchanges, like putting fluid into the cavity and removing it several times overnight. The patient is free of the fluid during the day time, making it a convenient option for patients.
Benefits
Benefits of Peritoneal Dialysis
Convenience & Flexibility
You can perform PD at home, work, or travel. It's an excellent option for people with busy lives.
Fewer Dietary Restrictions:
PD patients have more flexibility with food and fluids due to continuous treatment.
Less Impact on Lifestyle
PD patients often feel more in control and continue daily activities with minimal interruptions.
Risk & Considerations
- Infection: Since PD involves a catheter in the abdomen, there is a risk of infection, particularly peritonitis, which is an infection of the peritoneal lining. Proper hygiene and care are essential to prevent this.
- Fluid Balance: Even though PD offers more flexibilit y, it’s important to monitor fluid intake and output. Too much fluid can strain the heart and cause fluid overload in lungs.
- Potential for Weight Gain: The high glucose in the dialysate solution, can lead to weight gain. It’s important to monitor weight and talk to your healthcare provider about managing this.
- Training and Support: Patients and caregivers must be trained on how to perform the exchanges, care for the catheter, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Lifestyle Considerations
Dietary Management
PD offers flexibility, but a kidney-friendly diet with low sodium, potassium, phosphorus, and controlled protein is essential.
Exercise
Staying active with light exercise like walking or swimming boosts health and supports more effective dialysis.
Mental Health
PD offers home-based independence, and our center supports emotional well-being with complete, compassionate dialysis care.
Regular Checkups
Though PD is home-based, regular nephrologist visits ensure effective treatment and monitor your health progress.
Need Any Helps?
Get More Consultations
Take the first step towards better kidney health with expert nephrology care from Dr. Kosha Patel. Manage peritoneal dialysis confidently with compassionate, specialized treatment tailored just for you.
Contact Us
Lorem Ipsum is simply dumy text of the printing typesetting industry lorem ipsum.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis is a home-based treatment that uses the lining of your abdomen (peritoneum) to filter waste and toxins from your blood.
Which Dialysis is Best?
There’s no single “best” type — it varies by person.
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) may be best if you:
- Prefer to perform dialysis at home
- Have no preference for needles
- Desire greater freedom and flexibility
- Travel infrequently or hold a full-time job
- Wish for less intense treatment that functions more akin to natural kidneys
Hemodialysis (HD) may be ideal if:
- You prefer being treated by nurses in a clinic
- Find treatment difficult to control on your own
- Are medically not a strong candidate for PD (e.g., belly infection or surgeries)
Both are doing the same thing — cleaning your blood. The best option for you is based on your health, lifestyle, and what you feel comfortable with.
Is Peritoneal Dialysis Done Daily?
Yes, peritoneal dialysis is typically done daily.
There are two basic methods:
CAPD (Manual Method):
- Completed 3–5 times daily, each one lasting about 30–40 minutes.
- You do it yourself, no need for a machine.
APD (Nighttime Machine):
- Completed during sleep.
- The machine runs for approximately 8–10 hours at night.
Though it’s a daily routine, most people find it easy to incorporate into their lives.
Who Needs Peritoneal Dialysis?
PD is for individuals whose kidneys no longer function normally and must regularly be treated to rid their blood of waste products.
PD is a good match for individuals who:
- Would like to have dialysis at home
- Can enjoy flexibility and independence
- Are generally in stable health without severe complications
- May not tolerate hemodialysis well (for example, if they have low blood pressure or heart problems)
- Want to avoid regular trips to a dialysis centre
Your doctor will help decide if PD is a good option based on your health and lifestyle.
How Long is PD Dialysis?
This depends on the type:
- CAPD (Manual):
Each session takes around 30–40 minutes, done 3–5 times a day.
- APD (With Machine):
Reruns overnight as you sleep for roughly 8–10 hours.
It’s distributed throughout the day or nighttime, so for some, it feels more relaxed than sitting at a clinic in blocks of time.
Is PD Better than Hemodialysis?
PD may be better for some, but not necessarily for everyone.
PD Might Be Better If You:
- Prefer doing dialysis from home
- Dislike needles
- Have a less rigid schedule
- Would like to travel or work more conveniently
- Would have steady health
But Hemodialysis Would Be Preferable If You:
- Can’t care for PD at home
- Have stomach issues such as infection or scarring
Feel safer with trained staff working on your treatment
Working Hours
Monday to Saturday
09:00 AM to 09:00 PM
For Emergency
24 X 7
Your Kidney Health, Our Priority
Contact us
Lorem Ipsum is simply dumy text of the printing typesetting industry lorem ipsum.
Copyright © 2025 Dr. Kosha Patel
Designed by EEG Technogeeks